帖子
分享您的知识。
+10
Sui Move vs Aptos Move - What is the difference?
Sui Move and Aptos Move - two prominent implementations of the Move programming language. While both are rooted in the same foundational principles, they have diverged significantly in design, execution, and ecosystem development. To better understand their differences, we need to uncover some of their key aspects:
How do their runtimes differ?
Both Sui and Aptos implement their own custom Move virtual machines (VMs). How does this impact performance, scalability, and developer experience? For instance:
- Does Sui's runtime optimize for parallel execution differently than Aptos'?
- Are there notable differences in transaction lifecycle management or gas models?
What are the differences between their standard libraries?
The Move standard library is a critical component for building smart contracts. However, Sui and Aptos have forked their implementations, leading to divergence:
- Are there modules or functions unique to one implementation but absent in the other?
- How do these differences affect common use cases like token creation, NFTs, or decentralized finance (DeFi)?
How does data storage differ between them?
One of the most significant distinctions lies in how Sui and Aptos handle data storage:
- Sui uses an object-centric model, where each object has its own ownership and permissions.
- Aptos, on the other hand, retains a more traditional account-based model similar to Ethereum.
- How does this impact state management, composability, and gas efficiency?
Is it fair to say that Aptos is closer to EVM while Sui is closer to SVM?
Some developers argue that Aptos' account-based architecture resembles Ethereum's EVM, while Sui's object-centric approach aligns more closely with Solana's SVM.
- Do you agree with this analogy? Why or why not?
- How does this architectural choice influence developer ergonomics and application design?
Are there universal packages working for both Sui Move and Aptos Move?
Given their shared origins, it would be ideal if some libraries or tools were interoperable across both ecosystems.
- Are there any existing universal packages or frameworks that work seamlessly on both platforms?
- If not, what are the main barriers to achieving compatibility?
Can one of them be transpiled into another?
If a project is built on Sui Move, could it theoretically be transpiled to run on Aptos Move, or vice versa?
- What are the technical challenges involved in such a process?
- Are there tools or compilers currently available to facilitate this kind of migration?
- Move
答案
2让我们比较一下 Sui Move 和 Aptos Move. 这两者就像 Move 语言家族的兄弟姐妹,但他们肯定有自己的个性:
#他们怎么滚动?运行时差异:性能、可扩展性和开发者体验
Sui 和 Aptos 都实现了自定义 Move 虚拟机 (VM),这些虚拟机充当其运行时,影响性能、可扩展性和开发人员体验.
研究表明,Sui Move 就像那个总是四处奔波、快速把事情做好的朋友. 它的虚拟机是为速度而构建的——想想 0.5 秒就能锁定交易,这要归功于 DAG 设置中一些花哨的并行执行技巧(例如,0.5 秒,如 Aptos 与 Sui 对比运动:移动区块链对比 中所述)
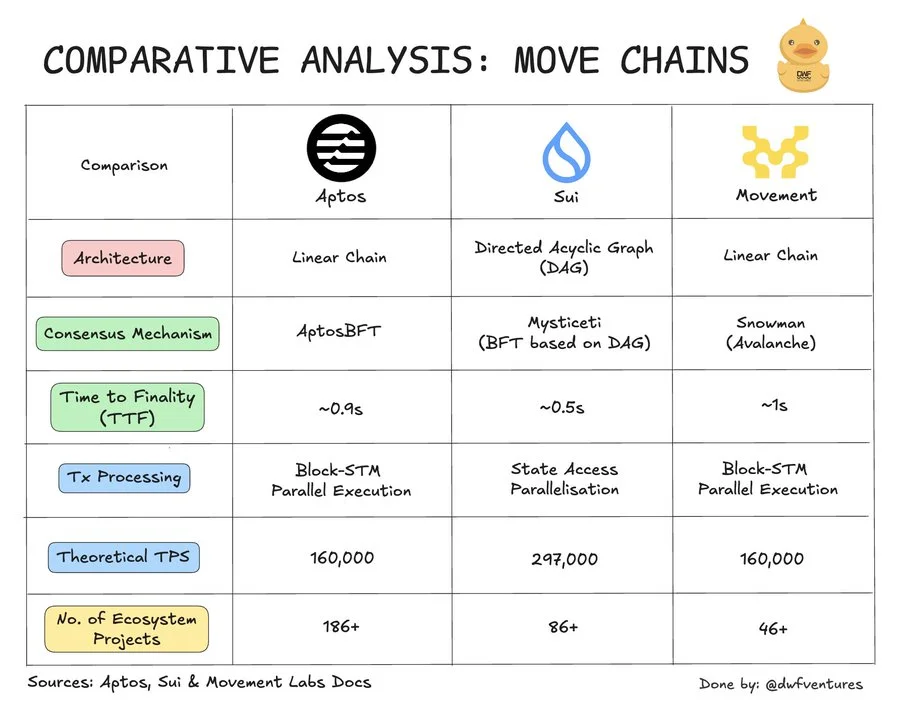
相比之下,Aptos采用具有并行执行能力的线性架构,但其对每笔交易的共识可能会导致大规模瓶颈,最终结果约为0.9秒.
Sui的因果排序意味着许多交易不需要完全共识,从而减少了延迟,而Aptos则使用了HotStuff的衍生产品AptosBFT,可确保快速完成,但可能会增加计算开销.
Sui的模型包括根据验证者输入在每个周期开始时设定的参考汽油价格,从而确保可预测性和低费用(例如,根据 [Sui vs Aptos:哪种区块链适合您?],平均交易费为0.0001美元)(https://www.cointranscend.com/sui-vs-aptos-which-blockchain-is-right-for-you/)).
标准库:模块、函数和用例
由于 Sui 和 Aptos 具有不同的架构设计——SUI 以对象为中心,将资产视为可转移对象,而 Aptos 基于帐户,将资产与账户关联——它们的标准库在结构和用法上有很大差异.
创建自定义代币
在Aptos中,来自aptos_framework标准库的managed_coin模块为创建和管理可替代代币提供了一种直接的方法. 下面是一个例子:
module example::MyToken {
use aptos_framework::managed_coin;
use std::signer;
/// Struct representing the custom token
struct MyToken has key { }
/// Initialize the token with name, symbol, decimals, and monitoring option
public entry fun initialize(account: &signer) {
managed_coin::initialize<MyToken>(
account,
b"MyToken", // Name
b"MTK", // Symbol
6, // Decimals
true, // Enable monitoring
);
}
/// Mint tokens to the caller's account
public entry fun mint(account: &signer, amount: u64) {
managed_coin::mint<MyToken>(account, amount);
}
}
这个用例创建了与账户相关的可替代代币,这在基于账户的系统(例如Aptos)中很常见.
在 Sui 中,su coini 标准库中的模块将令牌作为对象进行管理. 你可以创建一种货币并使用一个TreasuryCap物体来铸造硬币. 下面是一个例子:
module example::MyToken {
use sui::coin::{Self, Coin, TreasuryCap};
use sui::transfer;
use sui::tx_context::{Self, TxContext};
/// Struct defining the custom token type (with `drop` for currency creation)
struct MY_TOKEN has drop { }
/// Create a new currency and transfer its TreasuryCap and metadata
public entry fun create_currency(ctx: &mut TxContext) {
let (treasury_cap, metadata) = coin::create_currency(
MY_TOKEN {}, // Token type witness
6, // Decimals
b"MTK", // Symbol
b"MyToken", // Name
b"A custom token", // Description
option::none(), // Optional icon URL
ctx,
);
transfer::public_transfer(treasury_cap, tx_context::sender(ctx));
transfer::public_transfer(metadata, tx_context::sender(ctx));
}
/// Mint new coins using the TreasuryCap
public fun mint(
treasury_cap: &mut TreasuryCap<MY_TOKEN>,
amount: u64,
ctx: &mut TxContext
): Coin<MY_TOKEN> {
coin::mint(treasury_cap, amount, ctx)
}
}
铸造 NFT
Aptos 使用代币模块来管理集合中的不可替代代币 (NFT). 以下是创建收藏和铸造 NFT 的方法:
module example::MyNFT {
use aptos_framework::token;
use std::string;
use std::signer;
/// Create a new NFT collection
public entry fun create_collection(creator: &signer) {
token::create_collection(
creator,
string::utf8(b"MyCollection"), // Collection name
string::utf8(b"A collection of NFTs"), // Description
string::utf8(b"https://example.com"), // URI
true, true, true, true, true, true, true, true, true, // Mutability flags
);
}
/// Mint an NFT within the collection
public entry fun mint_nft(
creator: &signer,
collection: &string::String,
name: &string::String,
uri: &string::String
) {
token::create_token(
creator,
*collection,
*name,
string::utf8(b"Description"), // Token description
1, // Maximum supply (1 for NFT)
*uri, // Token URI
0, 0, 0, // Royalty settings
vector::empty(), // Property keys
vector::empty(), // Property values
vector::empty(), // Property types
);
}
}```
在结构化集合中管理独特的数字资产(例如艺术品),这在基于账户的 NFT 系统中很常见.
在 Sui 中,NFT 是独立的`objects`,具有唯一的 ID,使用`object`和`transfer`模块进行管理. 下面是一个例子:
```rust
module example::MyNFT {
use sui::object::{Self, UID};
use sui::transfer;
use sui::tx_context::{Self, TxContext};
use std::string;
/// Struct representing an NFT
struct MyNFT has key {
id: UID,
name: string::String,
uri: string::String,
}
/// Mint an NFT and transfer it to the sender
public entry fun mint(
ctx: &mut TxContext,
name: string::String,
uri: string::String
) {
let nft = MyNFT {
id: object::new(ctx), // Generate a unique ID
name,
uri,
};
transfer::transfer(nft, tx_context::sender(ctx));
}
}
利用 Sui 以对象为中心的灵活性创建和转移独特的资产(例如收藏品),将其作为独立对象. 这些差异意味着开发人员必须调整代码,从而影响开发时间和生态系统的互操作性.
数据存储:以对象为中心的模型与基于账户的模型
最重要的区别之一是数据存储. Sui 采用以对象为中心的模型,其中每种资产(例如代币、NFT)都是一个具有元数据、所有权和权限的对象,以唯一的 ID 存储在链上([对象模型 | Sui 文档](https://docs.sui.io/concepts/object-model)).This 模型允许并行状态更新,增强可组合性和气体效率,因为交易通常只需要一次账本更新(例如,传输一个对象会更新其状态,而不是多个账户).
相反,Aptos使用类似于以太坊的基于账户的模型,在该模型中,账户在全球存储中拥有资源,因此每笔交易都需要更新发送者和收件人账户([Aptos与Sui——The Tie](https://www.thetie.io/insights/research/aptos-vs-sui/)).

更接近 EVM 或 SVM?
Aptos是否更接近EVM(以太坊虚拟机)以及Sui是否更接近SVM(可能是索拉纳虚拟机)的问题需要澄清. Aptos基于账户的模型与EVM一致,更新每笔交易的账户状态,使以太坊开发人员熟悉该模型(Aptos与Sui:比较两个不断增长的第 1 层区块链).
但是,Sui 的以对象为中心的模型是独一无二的,无法直接与像 Solana 一样基于账户的 SVM 相提并论. 一些开发人员认为 Sui 在可扩展性方面与 Solana 相似,但这与其说是数据模型,不如说是性能. 因此,可以公平地说 Aptos 更接近 EVM,而 Sui 的模型则与众不同,与 SVM 不一致,这给这个类比提出了质疑.
通用包:兼容性和障碍
鉴于它们的共同起源,理想的互操作性将涉及通用包. 但是,研究表明不存在这样的软件包,因为标准库和数据模型的差异会造成障碍.
例如,如果不重写 sui:: coin(GitHub-pentagonxyz/movemate:Move 的模块构件库),使用 Aptos 的 aptos_coin 的软件包将无法在 Sui 上运行. 障碍包括特定平台的 API、对象与账户模型以及不同的虚拟机实现,如果不进行重大调整,就不可能实现无缝兼容.
以下是Sui Move和Aptos Move之间清晰明了的比较,显示了它们如何共享核心语言,但在运行时行为、数据模型和开发模式上有所不同.
🏃 运行时间:速度、可扩展性和交易流程
Sui 的运行时使用 DAG 模型针对并行执行进行了优化. 由于因果排序,许多交易跳过了全球共识,因此简单的转账可以在大约0.5秒内完成. 它专为高吞吐量和低延迟用例而构建.
Aptos还支持并行执行,但使用更严格的AptosBFT共识模型(基于HotStuff),因此每笔交易都要经过共识. 这提供了更强的一致性保证,但可能会稍微减慢速度——最终结果约为 0.9 秒.
简而言之: • 对于简单、独立的操作,Sui 速度更快. • Aptos更倾向于保持一致性,在每笔交易中达成更广泛的共识.
🧱 数据模型:以对象为中心与以账户为中心
Sui 的整个模型都围绕着物体展开. 链上的所有东西——代币、NFT甚至包裹——都是具有唯一ID的对象. 对每个对象的所有权进行跟踪. 这意味着: • 易于组合和模块化设计 • 一笔交易 = 一个物体变更 = 高效天然气 • 非常适合游戏、NFT 和可组合 DeFi
Aptos 坚持使用更熟悉的基于账户的模式. 账户拥有结构化资源,每笔交易都会更新发送方/收款人账户. 它更像以太坊: • 对于 Solidity 开发者来说很熟悉 • 状态一致性强 • 更适合传统代币流
所以: • Sui → 就像将资产作为独立实体进行管理一样 • Aptos → 比如管理与账户状态相关的余额
💰 代币创建:TreasuryCap 与托管币
在 Sui 中,你可以将代币定义为一个对象(MY_TOKEN),然后通过 TreasuryCap 将其铸造. coin:: create_create_currency 函数使您可以完全控制元数据和供应逻辑. 代币也是对象.
在 Aptos 中,你可以使用 managed_coin 模块. 它将代币绑定到一个账户,并通过资源访问跟踪供应.
摘要: • Sui → 代币是带有 UID 的对象,存在于链上 • Aptos → 代币是账户控制下的资源
🎨 NFT:集合与独立对象
Aptos NFT 使用与账户存储关联的 token:: create_token 在集合中铸造.
Sui NFT 是具有自己的 ID 和元数据的独立对象. 您可以像任何物体一样灵活地铸造和转移它们.
这意味着: • Aptos → 更适合精选藏品 • Sui → 更适合可组合、获得许可的 NFT(例如游戏物品)
🔧 开发者体验和互操作 • Sui 每个时代设定一次汽油价格 → 便宜 + 可预测 • Aptos 气体是动态的,但每次发射更精确
但是互操作很难. Shared Move 语法不等于共享包: • aptos_framework:: coin ⇒ sui:: coin • 基于账户的逻辑不容易移植到对象逻辑
这就是通用包尚不存在的原因. 即使有共同的根源,虚拟机/运行时的差异也迫使开发人员编写特定链的逻辑.
🔄 EVM 与 SVM 的比较 • Aptos 更接近 EVM — 账户模型,类似的状态更新 • Sui 不太像 Solana(SVM 也是基于账户的). 它独一无二,采用以对象为先的设计
因此,忘记类比了——Sui 在数据建模和执行方面独树一帜.
📦 团队如何处理兼容性
如果你正在构建跨链: • 每条链都需要适配器或单独的模块 • 像 MoveMate 或 Pentagon 这样的工具可以提供帮助,但完全互操作仍然意味着每次运行时都要进行编写 • 一些开发人员为了简单起见,首先使用 Aptos,然后转到 Sui 进行缩放和对象逻辑
TL; DR — Sui vs Aptos Move
Feature Sui Move 运行时并行,基于 DAG,sub-1 的终局性 BFT 共识,一致性强 数据模型以对象为中心基于账户 通过 TreasuryCap 对象通过账户中的 managed_coin 创建代币 NFT 独立、基于集合的可组合对象、与账户绑定 开发体验快速、可组合、全新模型熟悉、稳定、类似以太坊 基于 Epoch 的 Gas 模型参考价格每个 TX 定价 互操作性低,需要链特定的逻辑相同
你知道答案吗?
请登录并分享。
Move is an executable bytecode language used to implement custom transactions and smart contracts.